information system as it was perceived a few years back before, Rather than encompasses
the entire online of Developing, marketing, selling, delivering, serving and playing for
products and services transacted through the internet, e-Commerce broadly includes the
following tasks:
- Product information
- Requirement of the customer
- Purchase transaction
- Delivery of the product
- Digital platform as a service for customer
Thanks to digital transform, Role of the internet has been the major driving force to make
e-commerce possible. Thought e-commerce provides a number of benefits to the companies,
still, the majority of the commercial transaction take place through the traditional channels.
E-commerce has come a long way in the last decade, but there is a still a long way to go.
There are many dot-com companies in mid of 2000 had failed due to lack of infrastructure
and awareness, but now in digital age, now it can say that this is e-commerce age in digital
transformation. Today, millions of companies including large and small, are somehow
involving in e-commerce activities. Few giant companies such as Amazon, Alibaba, Flipkart,
Snapdeal and Wal-Mart etc, in e-commerce have captured the domestic and global
consumer and business market too.
e-commerce possible. Thought e-commerce provides a number of benefits to the companies,
still, the majority of the commercial transaction take place through the traditional channels.
E-commerce has come a long way in the last decade, but there is a still a long way to go.
There are many dot-com companies in mid of 2000 had failed due to lack of infrastructure
and awareness, but now in digital age, now it can say that this is e-commerce age in digital
transformation. Today, millions of companies including large and small, are somehow
involving in e-commerce activities. Few giant companies such as Amazon, Alibaba, Flipkart,
Snapdeal and Wal-Mart etc, in e-commerce have captured the domestic and global
consumer and business market too.
E-commerce also used to reduce the transaction cost, improve customer services, speed up
the flow of information from the manufacturing to the supplier to customer.
the flow of information from the manufacturing to the supplier to customer.
1. Categories of e-Commerce
- B to C: Business to Customers (B2C): This is meant for household customers. This model is built around providing convenience, quality and best value for money to the end users. eg: Flipkart
- B to B: Business to Business (B2B): This model is meant for the wholesalers and retailers who need some items which are unavailable in the local market. Eg: Alibaba
- C to C: Consumer to Consumer (C2C) In this model consumer selling directly to another consumer. Eg: eBay
- B to G (e G): Business to Government (B2G): In this model wholesalers directly sell or supply to the government
Where day to day smart-phone users are increasing, in mobile age for purchasing goods and
services electronically is also known as mobile commerce or m-commerce.
services electronically is also known as mobile commerce or m-commerce.
2. E-Commerce life cycle Business Model
Buying Process
This process allows users to search and buy different products listed by sellers.
Registration Fee
Manufacturers or Distributors pays the annual rent for registering to Storeyo.com. In order
to enlist their products or to put any kind of advertisements, the companies must be
registered. This is a fixed rent.
to enlist their products or to put any kind of advertisements, the companies must be
registered. This is a fixed rent.
Listing Fee
Manufacturers or Distributors pays the annual rent for listing each product. This is a
variable rent calculated keeping the cost and various other factors in mind.
variable rent calculated keeping the cost and various other factors in mind.
Service Charges
- Shipment
- Maintenance
- Discounts
Advertisements
The company allows different advertisements which are also a source of revenue.
The company allows different advertisements which are also a source of revenue.
4. Operations Model
A). Stock it yourself model
In this we are maintaining our integrated warehouses that are able to handle shipments to
web customers, so by keeping the warehouses, we are fulfilling the orders. Through this, we
have full control over the fulfillment process.
web customers, so by keeping the warehouses, we are fulfilling the orders. Through this, we
have full control over the fulfillment process.
B). Outsourcing warehouse model:
In this, we can use logistics specialists which do the work of stockpiling and shipping web
orders. So once an order comes into our site it is automatically transmitted to its warehouse
and directly shipped to the customer through courier.
orders. So once an order comes into our site it is automatically transmitted to its warehouse
and directly shipped to the customer through courier.
Firefly (customer profiles) as Seller agents They will make markets more accessible to
providers CyberCash & payU
They are payment enablers which handle purchase transactions and their related fund's
transfers, as well as risk management.
transfers, as well as risk management.
Time slots for delivery
You may have different time slots depending upon the demand of the customers. They are
categorized as for example:
categorized as for example:
2-3 days
5-7 days
Types of inventory
This is a key term in terms of cost effectiveness. It is the direction and control of activities
with the purpose of getting the right inventory in the right place at the right time in the right
quantity in the right form at the right cost.
with the purpose of getting the right inventory in the right place at the right time in the right
quantity in the right form at the right cost.
This is introduced in our inventory management with a purpose of preventing disruptions in
deliveries to customers.
deliveries to customers.
B). Lot size inventory
We are purchasing items in quantities greater than needed to take advantage of quantity
discounts, to reduce shipping and setup costs.
discounts, to reduce shipping and setup costs.
C). Cross docking
In this strategy, we can move our goods directly from our warehouses to consumers. This
distribution strategy we have applied in which the customers and distributors are supplied
(in the case of B2C & B2B) by central warehouses which act as coordinators of the supply
process and as transshipment points for incoming orders from distributors and consumers
but in this strategy we are not keeping any stock.
distribution strategy we have applied in which the customers and distributors are supplied
(in the case of B2C & B2B) by central warehouses which act as coordinators of the supply
process and as transshipment points for incoming orders from distributors and consumers
but in this strategy we are not keeping any stock.
D). Refresh inventory
We are constantly refreshing our inventories through the received orders and products
coming from the distributors. When a new lot of product comes to the warehouses then we
send those products to the customers which are already present in our warehouses and
through the various time slots we are continuously refreshing our inventories.
coming from the distributors. When a new lot of product comes to the warehouses then we
send those products to the customers which are already present in our warehouses and
through the various time slots we are continuously refreshing our inventories.
E). Transportation cost
This includes the cost of moving the items from the warehouse to warehouse and warehouse
to consumers. As seen from the diagram given below we have two slots for the
transportation costs. The overall transportation cost is thirty-one percent of the total capital
estimation.
to consumers. As seen from the diagram given below we have two slots for the
transportation costs. The overall transportation cost is thirty-one percent of the total capital
estimation.
i) Warehouse to warehouse
It includes the cost of moving the items from one warehouse to other. This will mainly occur
when the cost of moving goods from distributor to warehouse is high than the cost of moving
products among the warehouses. Example, when one consumer demand for any variety of
products and it’s not available in the nearby warehouse, then we order the product from the
nearby warehouse to avoid the high cost of ordering product from the distributor.
when the cost of moving goods from distributor to warehouse is high than the cost of moving
products among the warehouses. Example, when one consumer demand for any variety of
products and it’s not available in the nearby warehouse, then we order the product from the
nearby warehouse to avoid the high cost of ordering product from the distributor.
ii). Warehouse to customer
This includes the cost of shipping the products from the warehouse to the customers. As
shown in the graph we have warehouses in the areas where the demand is high and if some
item will not be available in the nearby warehouse then we will ship that item from the next
nearby warehouse. If the time slot is in 1 day or 2 days then we will ship the items directly
from the distributors using the cross-docking strategy.
shown in the graph we have warehouses in the areas where the demand is high and if some
item will not be available in the nearby warehouse then we will ship that item from the next
nearby warehouse. If the time slot is in 1 day or 2 days then we will ship the items directly
from the distributors using the cross-docking strategy.
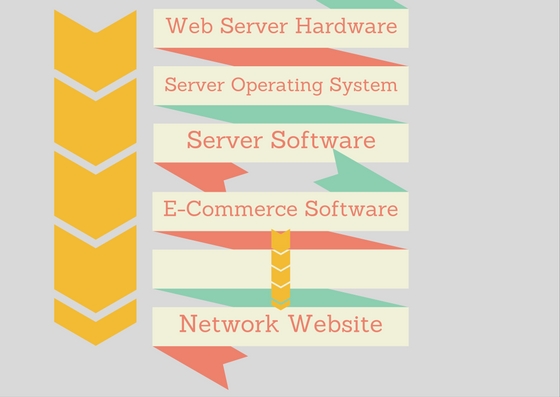
5. E-commerce Infrastructure:
i). Hardware:
A web server hardware platform is one of the main e-Commerce technology infrastructure
components.There are many features the web-server such as the storage capacity and
computing power etc,. depend upon the software that run on the server and the volume of
the e-commerce transactions to be proceed. The main guiding principle remains that there
must be adequate hardware back-up to avoid a major business disruption in case of a failure
of the primary web server.
ii). Software: Categorizes in two parts
a) Web-server:
A large number of functions such as identification retrieval and sending of webpage, website
tracking, website development,and web page development, the website must have
web-server software.
Example:
- Database
- Application Server
- Web Server
- Web Browsers
b) E-Commerce:
- Catalog management
- Product configuration
- Shipping Cart
- E-Commerce Transition
- Web Traffic Data Analysis
- Retail and Wholesale
- Marketing
- Finance
- Manufacturing
- Auctions
Electronic payment system:
- Electronic cash (e-Cash)
- Electronic Wallets (e -Wallets)
- Online Payment
- Plastic Money
- Cash on delivery (COD)
6. Management Challenges and opportunities
New Business model:
In mid of 2000, sudden burst of dot.com age. Termed as bubble burst. Doing business over
the internet is not necessary more efficient or cost effective than traditional business
model. Nowadays due to technology advancement and reform in business industry
e-commerce industry become a very ease to the business.
Required changes in business Process:
It should bechanges accordingly. Rule, regulation, polices and procedure should be
transparent and fare.
Channel Conflicts: Sometime distributor supplies product directly to the buyers.
Taxing, Legal and Regulatory for e-commerce:
E-commerce presents a major challenge for tax administrations, given the often multi-
jurisdictional nature of the transactions and the potential anonymity of the parties and it is
country specific.
jurisdictional nature of the transactions and the potential anonymity of the parties and it is
country specific.
E-commerce transactions should be legally straightforward. You get money up front for the
sale, in return for delivery of a product as described within the timeframe specified.
A standard set of terms and conditions should cover the vast majority of transactions.
sale, in return for delivery of a product as described within the timeframe specified.
A standard set of terms and conditions should cover the vast majority of transactions.
E-commerce is not only challenging traditional business methods but is also having a
massive impact on consumers’ habits. The growing importance of e-commerce and the
spreading of the Internet, which is having profound changes on almost all aspects of our
society and life, has recently called for the drafting of new legal instruments, both at global
and European level, in order to put the regulation of the Net on a more solid foundation and
to better regulate the activities carried out through this medium. It allows companies to
establish a global presence, which is of paramount importance for relatively small and newly
established entities who want to engage in cross-border trade. It offers competitive
advantages in respect to traditional methods of doing business. Forward-thinking companies
have grasped this truth and have opened their own website, confident of increasing and
enhancing their business and efficiency.
Security and privacy:
In an online business, everything is dependent on technology proper measures should be
taken to protect it from attackers or hackers. Several technologies can be employed to help
reduce the risk to companies and their customers when completing e-commerce
transactions.
Managerial opportunities:
E-Commerce provides a wide range of opportunities to the organizations. Managers can get
many advantages with the use of this technology. Internet revolution really reduces the
transaction cost: exchange of sales of goods and money bank guaranty.
Conclusion
Today e-commerce is not buying and selling a product or service platform online but it is big
information center or we can say that it becomes a big search engine for the most of the
things. E-Commerce technology infrastructure is very important is the key to successful
e-Commerce. Today e-Commerce is very advance and provides many
safeguards and secure in term customer and vendor too. E-Commerce provides huge
opportunities and ways of doing business online. In spite of that, there are many challenges
of pre to post sales and service.
information center or we can say that it becomes a big search engine for the most of the
things. E-Commerce technology infrastructure is very important is the key to successful
e-Commerce. Today e-Commerce is very advance and provides many
safeguards and secure in term customer and vendor too. E-Commerce provides huge
opportunities and ways of doing business online. In spite of that, there are many challenges
of pre to post sales and service.














This is very informative article regarding the E-Commerce.
ReplyDeletethanks for your feedback
Delete
ReplyDeleteI every time spent my half an hour to read this blog's content daily along with a mug of coffee. netflix login